TL;DR: Pivot by setting up a portproxy between your machine and a machine in another network using netsh interface portproxy add v4tov4 listenport=<port in> connectport=<port out> connectaddress=<destination>.
Let’s say machine A has access to a Windows machine, B, which has an additional interface configured to reach machines in another (internal) network, including machine C. As our machine A cannot directly talk to machine C and vice versa, what can we do to pick up files hosted on our machine A from machine C, or do further reconnaissance of C from A?
One quick and easy way is to configure a “portproxy” on machine B, which listens on a specified port and sends incoming traffic on to machine C or A (depending on the use case). Let’s have a look on how to do that for an IPv4 to IPv4 configuration.
For this example we have:
- A at 192.168.1.2
- B at 192.168.1.3 and 10.10.10.3
- C at 10.10.10.4
Setup on machine B
On machine B, execute the following:
netsh interface portproxy add v4tov4 listenport=1337 connectport=8000 connectaddress=192.168.1.2
Here, we are setting up a portproxy that will listen on port 1337 and send the received data to the connectaddress (A) on port 8000. This is done via a separate TCP connection, as you can observe via Wireshark.
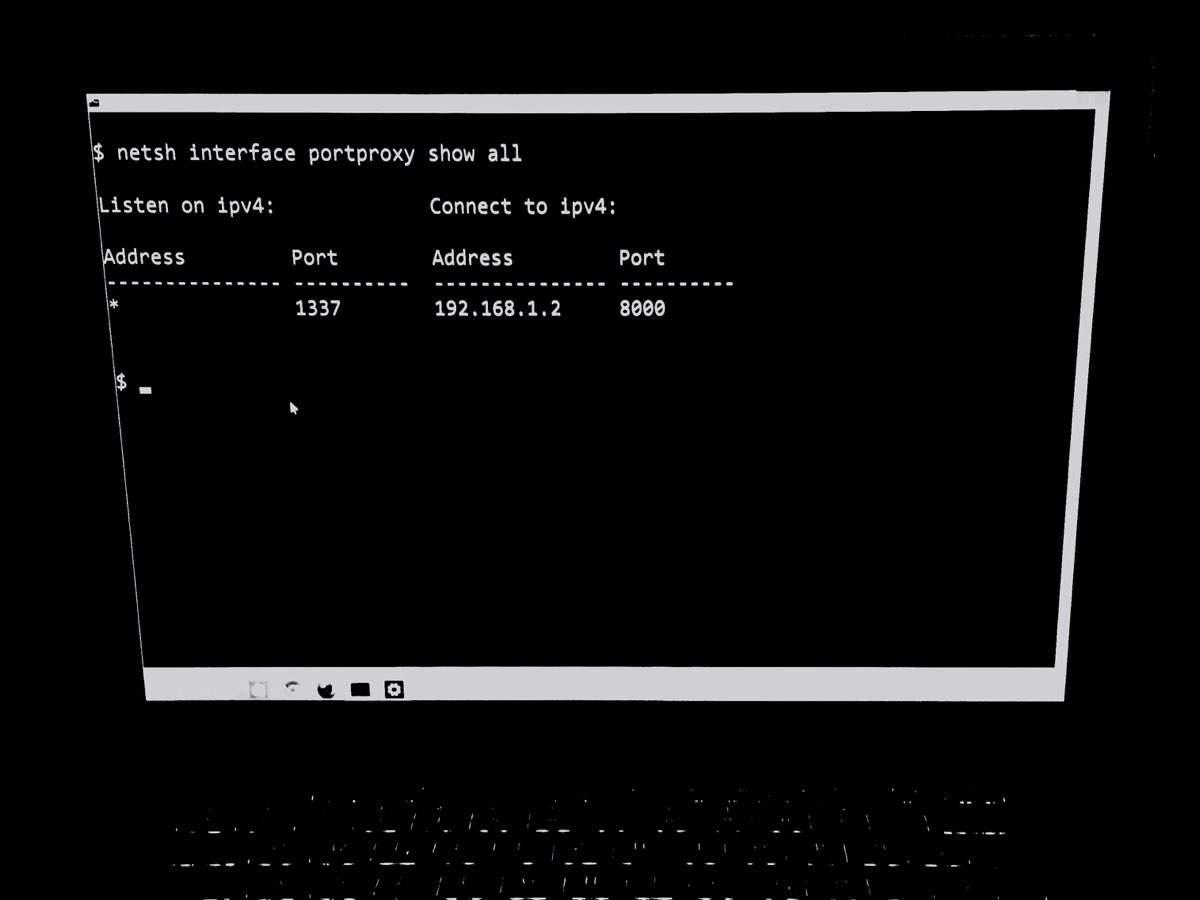
Let’s verify the setting looks good with netsh interface portproxy show v4tov4.
Listen on IPv4: Connect to IPv4:
Address Port Address Port
--------------- ---------- --------------- ----------
* 1337 192.168.1.2 8000
Note that the portproxy config will be stored in the registry, so this is the place where you can detect persistent portproxies without using netsh.
Get-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\PortProxy\v4tov4\tcp
*/1337 : 192.168.1.2/8000
...
To be able to try it out, let’s poke a hole into our firewall (still on B):
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Proxy all the things" dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=1337
Setup on machine A for hosting
On our machine A we will now start a webserver and host a file:
python3 -m http.server 8000 in a directory with a test.txt containing Hello from A.
Fetch from machine C
On our machine C let’s write up a short download cradle to fetch and then output the file’s content from machine A:
powershell.exe -c echo (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.10.3:1337/test.txt')
Machine C will now reach out to B (10.10.10.3) on port 1337, which will reach out to A on port 8000 to fetch test.txt. We can see a hit from 192.168.1.3 in our Python webserver console and the results of test.txt printed on machine C.
Naturally, this also works in the other direction (A reaching C through B). Just set up the the right connectaddress and connectport.
To remove the portproxy, you can use delete v4tov4 like so:
netsh interface portproxy delete v4tov4 listenport=1337
And to remove the firewall rule again:
netsh advfirewall firewall delete rule name="Proxy all the things"
netsh on modern systems. Unfortunately, I haven’t found a simple way/Cmdlet to setup a portproxy in PowerShell. Do you know how? Please let me know.
✉️ Have a comment? Please send me an email.